Use AWS? Then Protect AWS
Amazon Web Services has several storage services within its public cloud platform which thousands of customers are taking advantage of every day. They have Elastic Block Store (EBS), Elastic File System (EFS), Simple Storage Service (S3), Glacier, Storage Gateway and much more. As organizations move more and more of their workloads to AWS, their data can get distributed across both on-prem data centers, AWS availability zones and across multiple AWS services. While there are many third-party vendors that can assist in creating backups for cloud services, customers may find it more cost-effective to use native solutions instead. If they use AWS, they want to protect AWS. To protect AWS resources, AWS has created its own native service to assist in backing up AWS resources, known as AWS Backup, which was announced in Q1 of this year.
What is AWS Backup?
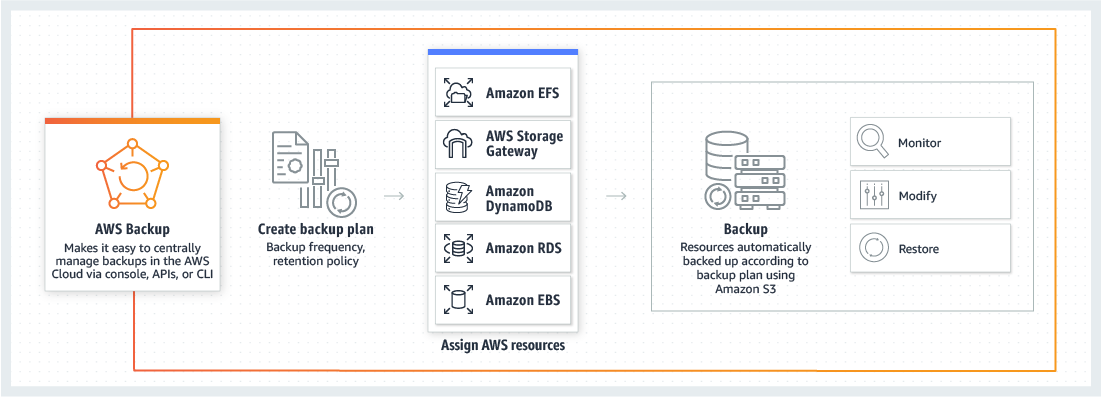
AWS Backup is a managed backup cloud service that makes it simple to consolidate and automate the backup of an organization’s data across various AWS services and on-prem resources. While you can definitely create your own backup strategy using scripts and the built-in snapshot tools, it can quickly become challenging to accommodate and maintain an enterprise-scale backup strategy. AWS Backup is designed to help you automate and manage your backups in one central place. The AWS Backup service currently supports EBS volumes, RDS databases, DynamoDB tables, EFS file systems, and even on-premises data through an integration with Storage Gateway.

What is so great about AWS Backup?
AWS Backup is designed to help simplify your backups using policy-driven backup plans. With AWS Backup, once you create the backup plans, you can apply the plans to resources using tags, automate backups using schedules, set backup retention policies, monitor backup activity, apply lifecycle management and much more. Backup uses Amazon’s highly-durable and cost-effective storage service, Simple Storage Service (S3), to store the backups. S3 is known as one of the most highly durable, scalable, secure and mature public cloud storage platforms. It has low-latency, high-performance throughput and designed with redundancy in mind. Some of the other benefits of AWS Backup is that it can be utilized for cloud-only environments, hybrid-cloud environments and can even be utilized in an on-premises environment.
How can you get started using AWS Backup?
AWS Backup is really simple to use and anyone can get started with it in minutes. Backup is another service that is available from the AWS Console or through the AWS Command-Line interface. When in the Backup service, all you need to do to start the service is to first create a backup plan. A backup plan defines the parameters of the backup policy, such as how often you want to back up the resources and how long to store the backups. Here you can decide if you want the backup to run as frequently as every 12 hours or less often such as every other week or month. You can also schedule how long to keep the backups and when to lifecycle and expire them. After creating the backup plan, you need to assign the AWS resources to the backup plan using tags. AWS Backup will automatically start backing up and managing these resources. Once resources have been backed up, you can monitor, restore and modify the backups. It’s just that easy.
Can your organization benefit from AWS Backup?
Any organization that wants to back up their data sitting across various AWS cloud services can utilize the AWS Backup service to store their data durably and securely using S3. Whether an organization is using EBS or EFS or utilizing the Storage Gateway to enable their on-prem application to use AWS features, they can all use AWS Backup to securely back up their data. At this time, Backup is supporting EBS, RDS, EFS, DynamoDB and Storage Gateway, but has plans to add additional services over time. AWS Backup is also a great way for organizations that are not already taking advantage of cloud efficiencies to get started on their cloud journey.